Sovereign Accession
Accession describes the event of a new Sovereign taking the throne upon the death of the previous King or Queen.
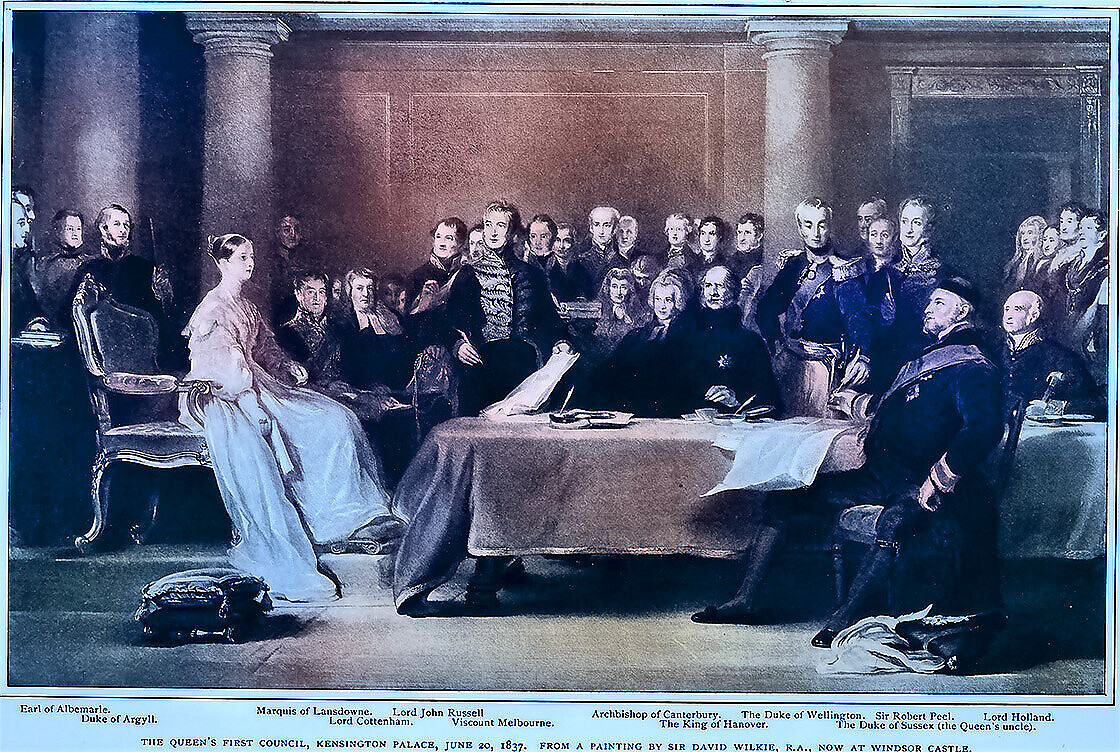
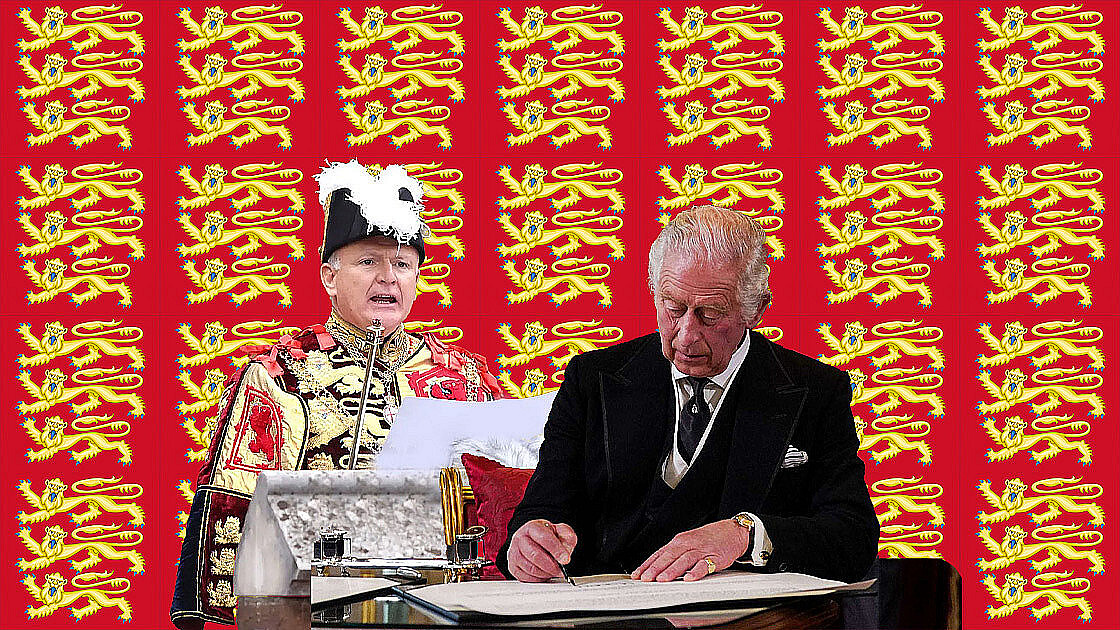
A new Sovereign succeeds to the throne as soon as his or her predecessor dies and is proclaimed as soon as possible at an Accession Council in St James's Palace.
Formed of certain Privy Counsellors, Great Officers of State, the Lord Mayor and High Sheriffs of the City of London, Realm High Commissioners, some senior civil servants and certain others invited to attend. The Council is held (without the Sovereign) to formally announce the death of the Monarch and proclaim the succession of the new Sovereign, and to make certain consequential Orders of the Council mainly relating to the Proclamation.
Following the proclamation, the Sovereign reads a declaration and takes the oath to preserve the Church of Scotland. The oath known as the accession declaration - an oath to maintain the established Protestant succession - is normally made at the next State Opening of Parliament.
In London, the public proclamation of the new Sovereign is first read out at St James's Palace.
The proclamation is also read out publicly in Edinburgh, Cardiff and Belfast. In each city, the accession is traditionally proclaimed at several different spots.
If the monarch is under 18 upon succeeding to the throne, there is provision for a regent to be appointed to perform the Royal functions. This can also happen if the monarch is totally incapacitated.